Acne & Rosacea
ACNE VULGARIS
What is acne?
Acne is an inflammatory disease of the sebaceous follicles that occurs primarily during puberty and is the most common dermatological disease worldwide. In addition to the face, the back and chest can also be affected by the typical blackheads, pustules and papules. Common acne of adolescence (Acne vulgaris), with occasional pustules, and or so-called “blackheads” (Acne comedonica) and its more severe forms such as acne papulopustulosa or acne conglobata, there are special forms such as acne inversa (Hidradenitis Suppurativa), medication-associated acne or acne rosacea and other forms.
Causes of acne
Acne is favored by several factors at the same time. The influence of hormones during puberty (androgens) leads to an enlargement of the sebaceous glands and increased sebum production. The latter also leads to an increased production of keratinocytes (horn cells), which causes the sebum follicles to be displaced. Since the sebum masses can no longer drain freely, congestion occurs and comedones (so-called blackheads) form. At the same time, the bacteria that live there (above all Propionibacterium acnes) present ideal conditions for proliferation, thereby leading to inflammatory reactions. Inflammatory pustules (acne pustulosa) which can also burst open spontaneously and, depending on the severity, can also reach deep into the skin (Acne conglobata).
How do you treat acne?
Depending on the severity, a step-by-step treatment plan follows.
Onset of action: The effect only occurs after 3 weeks, with an apparent worsening of the symptoms at the beginning with a temporarily increased occurrence of skin blemishes as well as redness, scaling or burning. These symptoms are often misinterpreted by the patient as intolerance, but usually appear after a few weeks of treatment.
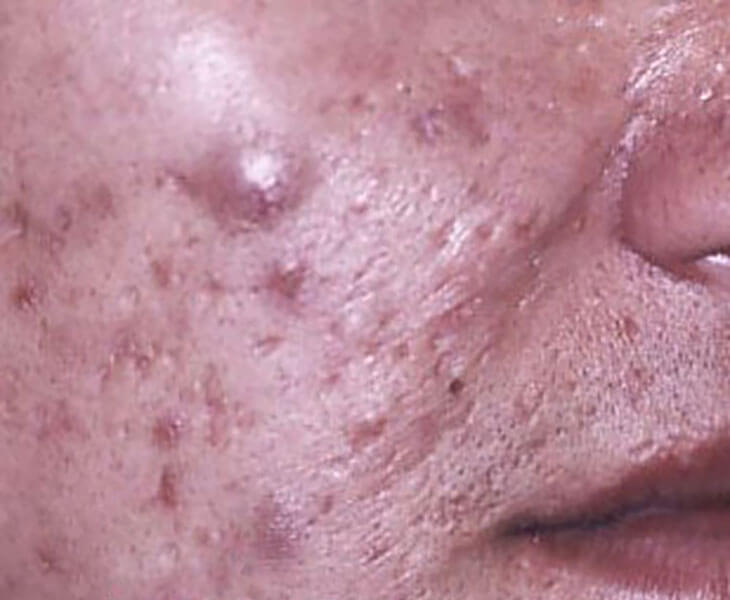
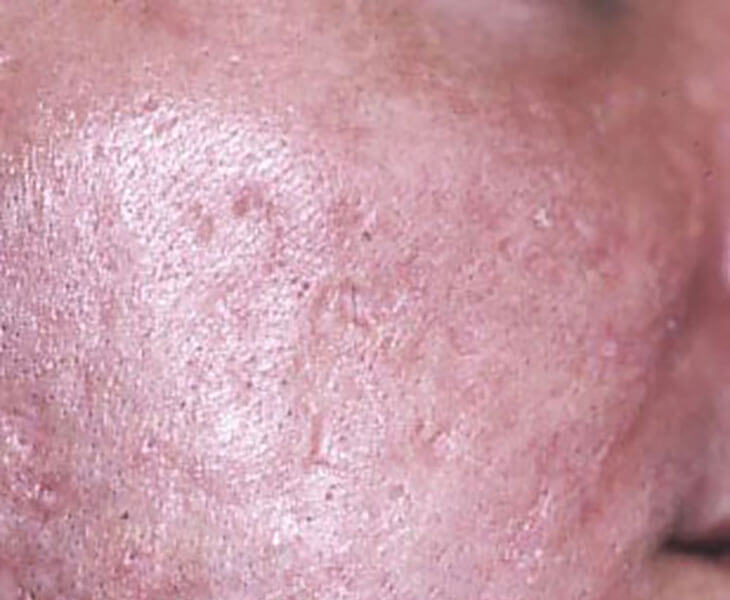
Drag the arrows to view the before and after pictures.
Acne and Diet
High-calorie foods with a high glycemic index and dairy products have long been suspected of having a negative impact on the course of acne. The extent to which such diets make sense is still the subject of debate.
Acne inversa (hidradenitis suppurativa)
Acne inversa is not part of the classic acne group. In contrast to the usual acne of adolescence, acne inversa usually only appears in adulthood and affects men more often than women. The exact cause is still unclear to this day, but a noticeably frequent occurrence of the disease can be observed in heavy smokers and overweight people. It is based on an often simultaneous inflammation of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles in the intertriginous areas (armpits, neck, groin region, anal folds, external genitalia, submammary region, hairy scalp). This leads to nodulo-cystic inflammation and abscesses, which in the further course lead to the formation of fistula tracts due to scarring and thus chronic areas of inflammation. The latter can then usually be managed neither by local nor systemic antibiotic or antiseptic therapy measures. Even retinoids, which are so effective in severe acne, have little effect. Often only surgical measures are helpful, whereby the inflammatory scarred areas are resected en bloc. As with other auto-inflammatory diseases, a glimmer of hope is provided by the so-called biological therapies, which have already been approved with TNF blockers.
ROSACEA
What is rosacea?
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory disease of the facial area, which is characterized by the occurrence of redness, papules and pustules, and in severe cases also by the formation of lumps. Due to the acne-like character with pustules, a so-called acne rosacea spoken.
Causes of Rosacea
The disease tends to run in families and mainly affects adults, with people with light skin and smokers appearing to be at increased risk. Several factors are likely to play a role in its origin and formation. In addition to an increased expression of antimicrobial peptides (cathelicidins), there are also increased numbers of demodex mites in the skin of rosacea patients (demodex folliculorum), a natural commensal of the hair follicles of human skin. The facial redness resulting from the pathological vasodilatation also seems to be related to these factors.
How is rosacea manifested?
Various stages in the course of the disease are described, although not all stages necessarily have to be gone through or reached.
Stage I
stage II
Stage III
How do you treat rosacea?
Light forms:
Depending on the severity, local antibiotics (metronidazole) or local therapeutic agents against mite infestation ( ivermectin , permethrin) are used here. However, since these have no effect on the existing redness, some local therapeutics have already been approved for their isolated treatment in recent years. The therapeutic effects of the latter are still mixed. In some cases, laser treatment can help here. Local cortisone should only be given for a short time, if at all, since long-term therapy leads to a worsening of the symptoms.
Heavy Forms:
Here, systemic therapies with low dose tetracyclines show good results. Systemic retinoids, such as those used in acne therapy, can also improve the condition, but are not yet approved. The treatment of rhinophyma usually requires a surgical procedure using dermabrasion or an ablative laser.
Perioral dermatitis
Because of its similarity to rosacea, this disease is also often referred to as rosacea-like dermatitis and is therefore mentioned here. It occurs most commonly in young women, is a cause of overuse of topical care products, and clinically resembles mild rosacea.
Alone the omission of excessive care with various creams and ointments usually leads to healing. In the case of pronounced forms, local therapeutic measures, such as with rosacea, and antimycotics, such as with fungal diseases, are used.
Incidentally, it should also be mentioned that frequent manipulation with the hands on the face (exogenous contamination) also maintains or worsens the symptoms and is therefore absolutely to be avoided.
Due to the recent mandatory wearing of mouth and nose protection for current events, an increased occurrence of perioral dermatitis can also be observed in certain people!
Individual consultation
Individual consultation: We would be happy to consult you extensively on the individual examinations and treatment options in one of our offices. You are also welcome to schedule an appointment online.
ACNE INVERSA
Was ist Acne inversa (Hidradenitis suppurativa)
Acne inversa zählt trotz des ähnlichen Namens nicht zum Formenkreis der klassischen Akne. Im Gegensatz zur gewöhnlichen Akne des Jugendalters, tritt die Acne inversa meist erst im Erwachsenenalter in Erscheinung und betrifft Männer häufiger als Frauen. Die genaue Ursache ist bis heute unklar, jedoch kann ein auffällig häufiges Auftreten der Erkrankung bei starken Rauchern und übergewichtigen Menschen beobachtet werden. Zugrunde liegt eine oft gleichzeitige Entzündung von Talgdrüsen und Haarfollikel in den intertriginösen Arealen (Achselhöhlen, Nacken, Leistenregion, Analfalte, äußere Genitale, submammär Region, behaarte Kopfhaut). Hierdurch kommt es zu nodulo-zystischen Entzündungen und Abszessen, welche im weiteren Verlauf durch Vernarbung zur Ausbildung von Fistelgängen führen und dadurch chronische Entzündungsareale entstehen. Letztere können dann meist weder durch lokale noch systemische antibiotische oder antiseptische Therapiemaßnahmen bewältigt werden.
Auch Retinoide welche bei der schweren Akne so effektiv sind zeigen kaum Wirkung. Häufig sind nur noch chirurgische Maßnahmen, wobei die entzündlich vernarbten Areale en bloc reseziert werden, hilfreich. Einen Hoffnungsschimmer stellen, wie auch bei anderen auto-entzündlichen Erkrankungen, die sog. Biologika-Therapien welche mit den TNF-Blockern bereits ihre Zulassung erlang haben.
