Venous thrombosis
In venous thrombosis, a vein becomes blocked by a clot. The cause of a thrombosis can be varied. Immobility due to illness, operations, after childbirth and sitting for long periods (long-haul flights – travel thrombosis) are often the cause of thrombosis. Hormone treatments (the pill) also increase the risk of thrombosis. Some patients have an inborn error of certain coagulation factors (APC resistance, lack of antithrombin III, protein C and S). A thrombosis can also develop in severe diseases (inflammation, cancer) and is often an indication of the underlying disease.
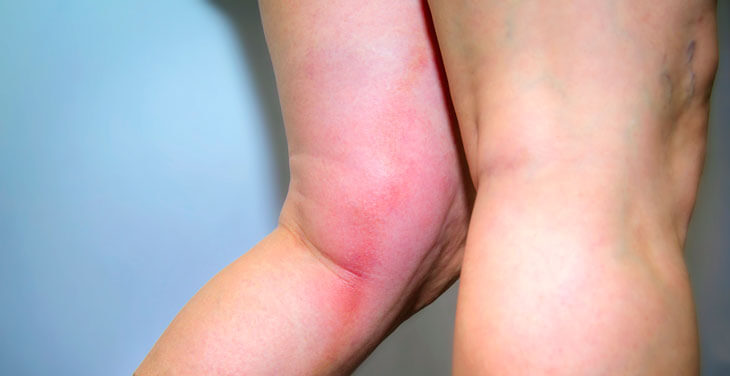
Thrombosis of the superficial veins:
There is a painful reddening and hardening along a superficial vein. The therapy depends on the extent of the thrombosis and the size of the affected vessel. In the case of minor phlebitis, local measures such as heparin ointments and wearing a compression stocking are sufficient. In some cases, therapy with blood-thinning medication is necessary.
Deep vein thrombosis:
This is much more serious as 90% of the venous blood in the legs flows through the deep veins of the legs. There is a hard and bulging swelling of the affected leg. The leg is tender and often blue in color. After a diagnosis with the vascular ultrasound, therapy with blood-thinning medication is initiated in any case. Wearing a compression stocking is an important therapy for the accompanying leg swelling and supports the breakdown of the blood clot in the vein.
Individual consultation
Individual consultation: We would be happy to consult you extensively on the individual examinations and treatment options in one of our offices. You are also welcome to schedule an appointment online.
